Dry-field Farming
Sustainable Dry-field Farming Using an Integrated System with Automation and Data Use
Building an Integrated Smart Agriculture System for Dry-field Farming
As the global population grows, food demand continues to rise. Modern agriculture must address this challenge by improving quality and prioritizing environmental sustainability, all while facing a shrinking workforce caused by aging populations and labor shortages.
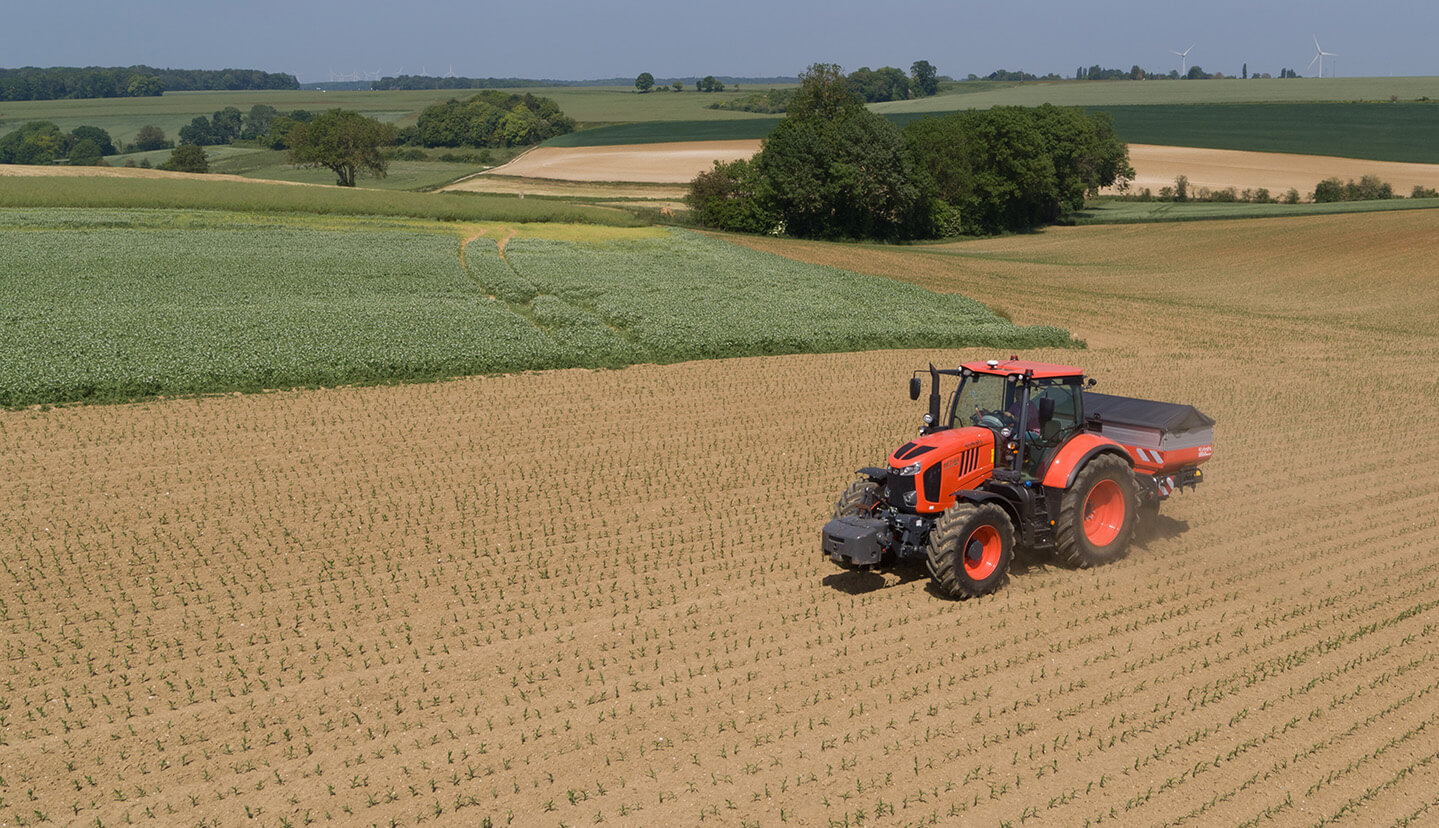
Kubota is taking on initiatives to achieve sustainable agriculture that meets three criteria: high-efficiency, high-quality, and lower environmental impact. In dry-field farming, which includes grain and vegetable production, Kubota offers products and solutions that reduce labor and ease workloads through data-driven precision farming and unmanned, automated operations in order to build an integrated smart agriculture system for dry-field farming.
An Approach Using a Precision Farming System and Unmanned Automate Agricultural Machinery for Both Rice and Dry-field Farming
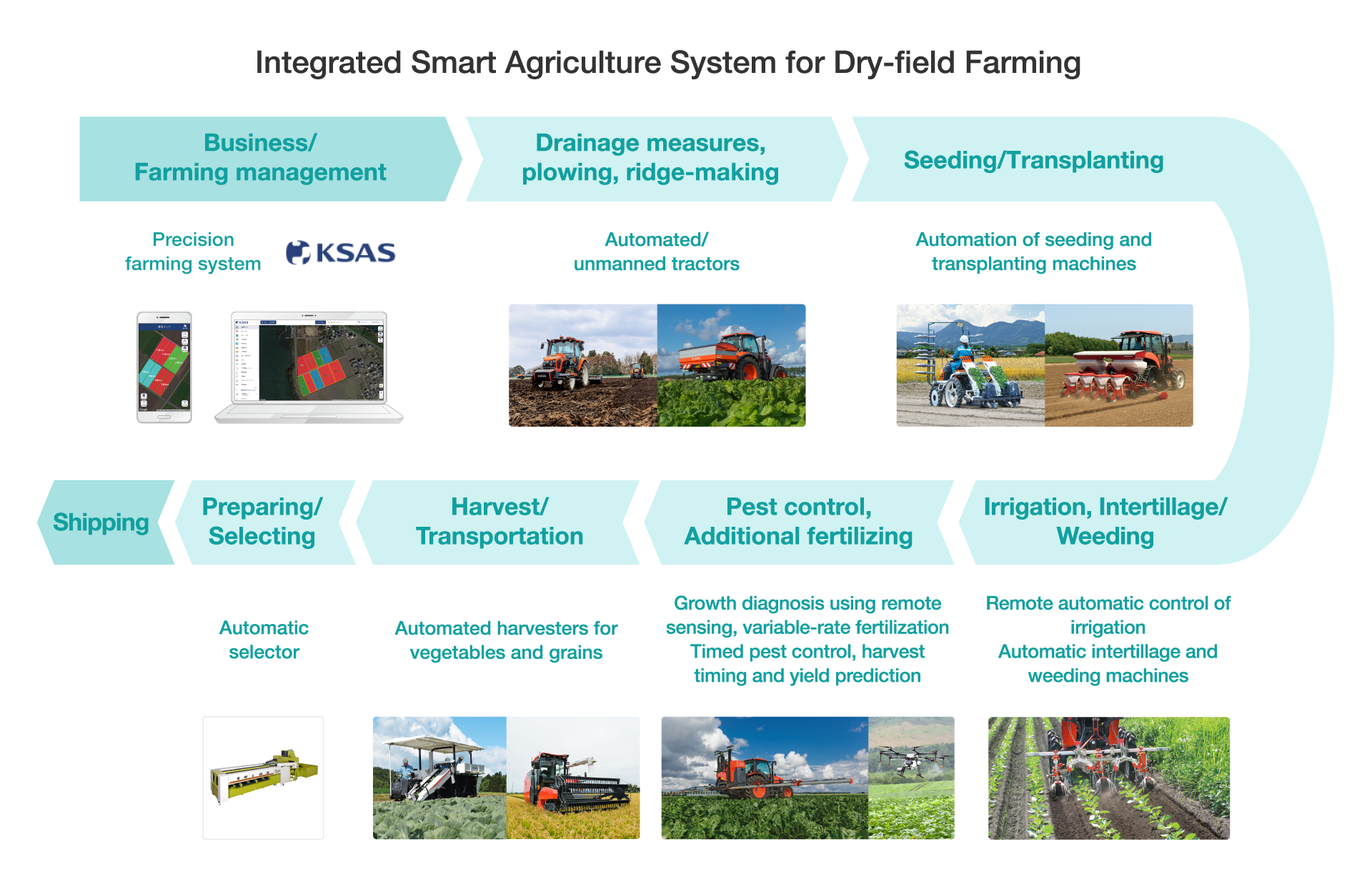
In the integrated smart agriculture system for dry-field farming, Kubota provides a precision farming system (Farm Management Information System, FMIS) that links data with a series of crop production processes, and unmanned automated agricultural machinery that reduces labor and workforce needs in each process.
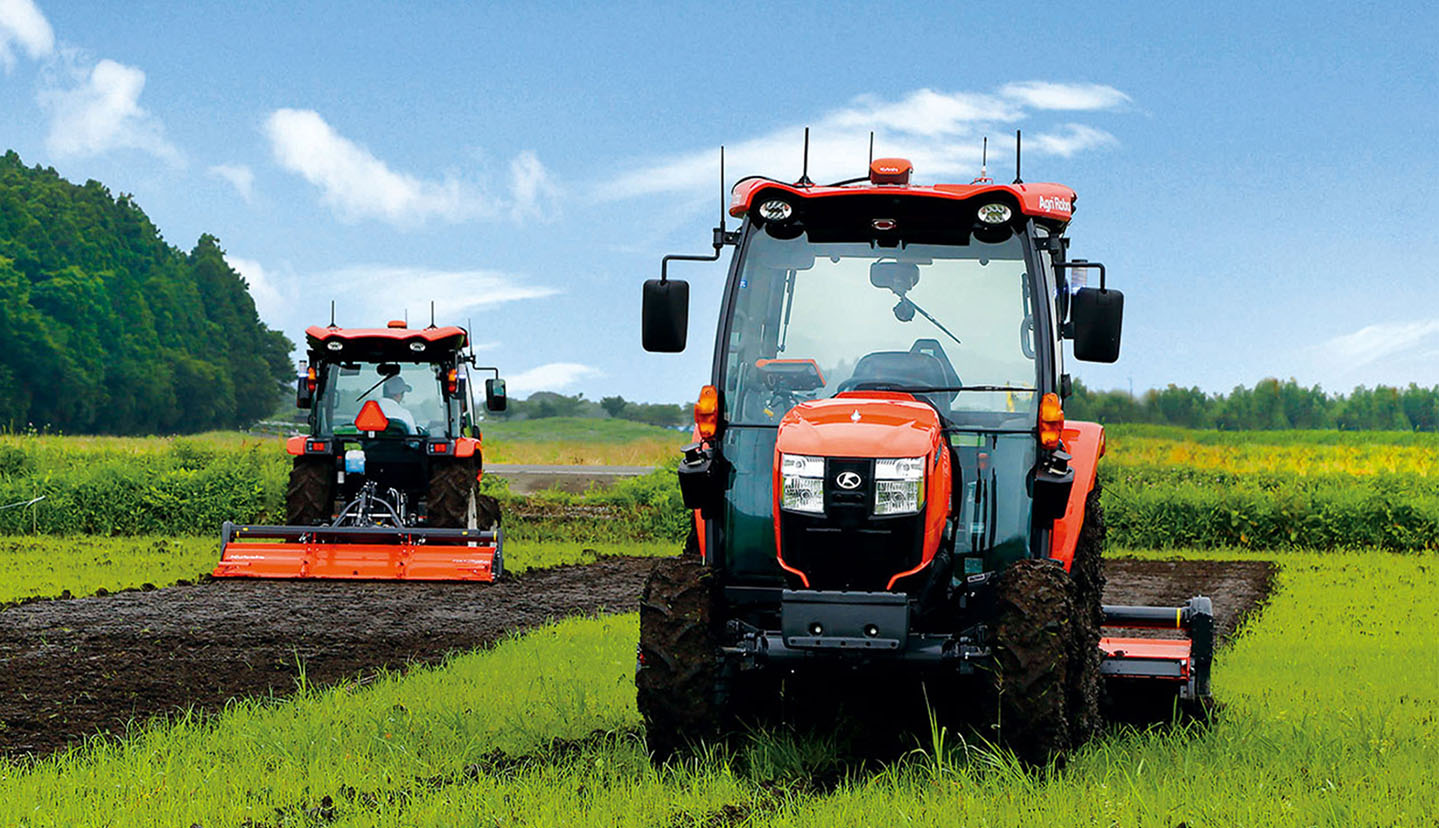
In farming based on this integrated smart agriculture system, an FMIS that analyzes field information, work records, past cultivation data, and other information is used to formulate optimized planting and work plans. Based on these plans, unmanned automated agricultural machinery replicates the skills of expert farmers in each process from tilling and ridge-making to harvesting, reducing labor and lightening workloads. While this work is performed, the unmanned automated machinery, drones, and other devices conduct remote sensing to collect data on crop quality, yields, and other elements, and this information is utilized by FMIS to formulate planting and work plans for the following year. This is repeated as a PDCA cycle with the aim of achieving desired yield and quality. Volumes of chemical pesticides and fertilizers are also optimized to ensure environmentally friendly dry-field farming.
From Seeding to Irrigation and Sorting: Developing the Automation Technologies Required for Dry-field Farming
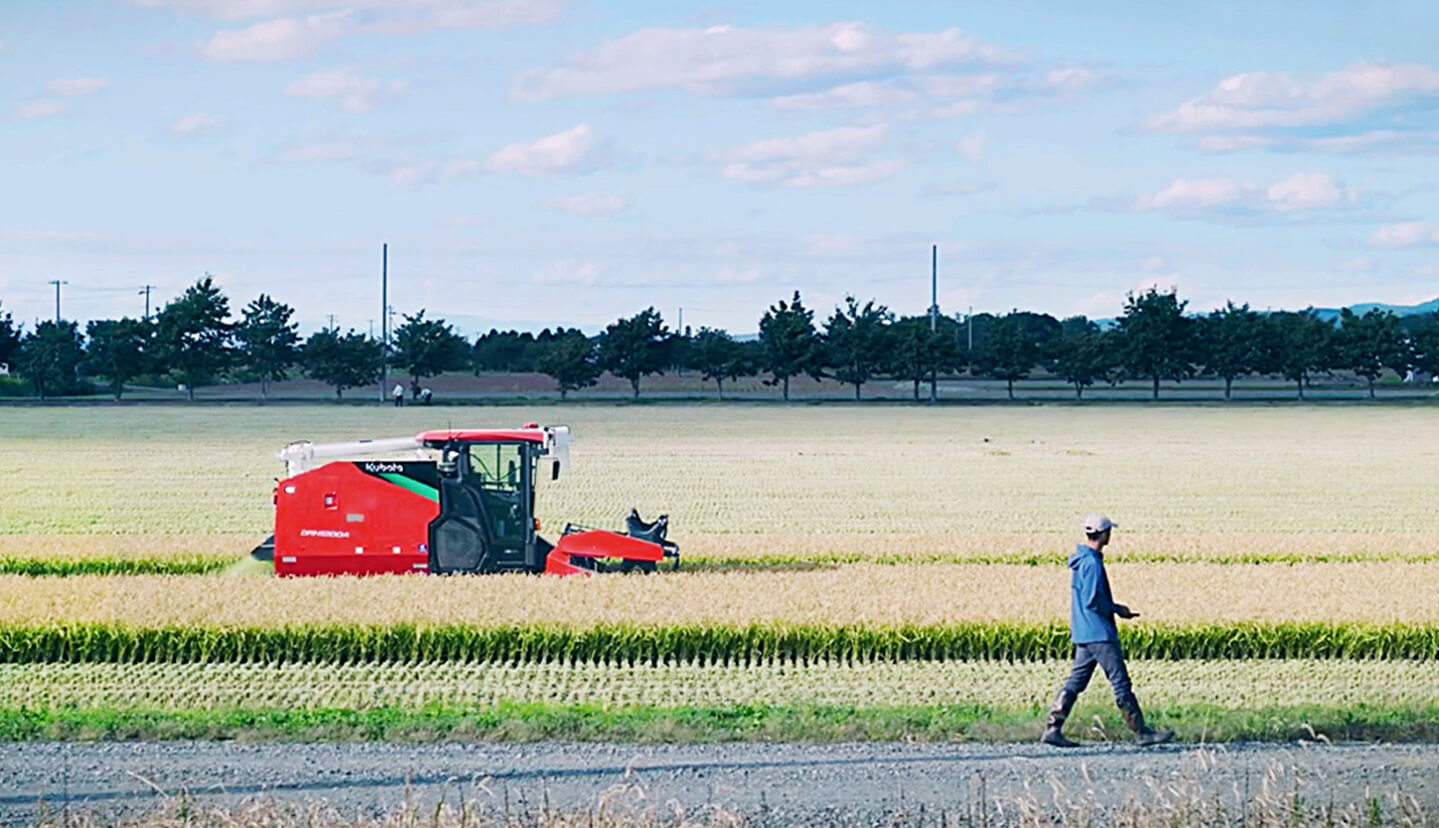
Along with FMIS and unmanned automated agricultural machinery, Kubota offers solutions that automate seeding and transplanting machines, enable remote irrigation control, and automate crop transportation and sorting, helping to make dry-field farming smarter.
One example of the solutions is in implements. Implements connect to tractors to make various tasks possible and serve as indispensable tools for dry-field farming. These implements connect smoothly to autonomous and unmanned agricultural machinery to make tasks such as plowing, seeding, and fertilization more precise and efficient. Kubota, which has carefully studied how agriculture is practiced in close consultation with farmers, is uniquely able to develop and provide both hardware and software solutions needed to make dry-field farming smarter through integrated technologies.
Through these solutions, Kubota is working to further advance and establish an integrated system that enables PDCA-model precision agriculture in grain, vegetable, and fruit farming so that anyone can produce high-quality crops.